Q4 2024 Investment Commentary
![]() Contributed by: Angela Palacios, CFP®, AIF®
Contributed by: Angela Palacios, CFP®, AIF®
 Contributed by: Nicholas Boguth, CFA®, CFP®
Contributed by: Nicholas Boguth, CFA®, CFP®
Think back to one year ago. It's January 2024. So far, the economy had avoided the recession everyone thought was coming. The S&P 500 just wrapped up a +26% year. Bonds provided some positive performance. Inflation was coming down, unemployment was still at historic lows, and the mood could be described as cautious optimism as investors expected a "growing but slowing" economy.
Most market forecasts (more on these later) expected 2024 to be good but definitely not great. ESPECIALLY in an election year, because you never know what sort of uncertainty that could bring!
Well, we just wrapped up 2024. How was it? From the lens of the financial markets, it was a strong year.
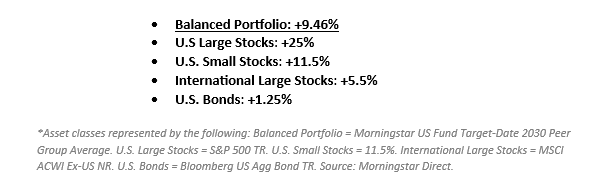
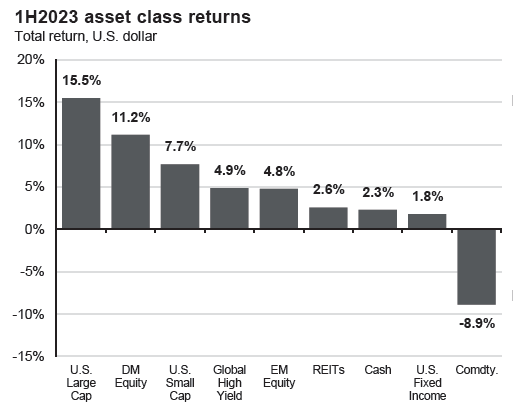
Stocks continued to climb, and bonds were slightly positive despite some bond market volatility. The S&P 500 was the standout among the major asset classes, but even small cap stocks and international stocks contributed positive performance.
Q4 brought some volatility and uncertainty between a major presidential election and multiple Fed rate cuts. U.S. stock indices climbed through the uncertainty, but international stocks and bonds fell slightly.
The big change during Q4 was the increase in bond yields as investors adjusted to what is looking like an even stronger economy than expected. A stronger economy generally comes with higher bond yields, which means less rate cuts from the Fed. This was reiterated in the Fed's Summary of Economic Projections in December that showed they expected the Fed Funds Rate to get to 3.9% by the end of 2025 (3 months prior, that projection showed an estimate of 3.4%).
We'll be watching this dynamic continue to evolve in the markets this year, but as of today investors are looking at a strong economy backed by an easing Federal Reserve, positive expectations for stock earnings, and decent bond yields providing strong fixed income options.
Interest Rates and The Economy
In December, the Federal Reserve (the Fed) held its final meeting of 2024, finalizing a year marked by significant continued disinflation and one of the strongest in recent years of economic activity. However, uncertainty always remains when looking ahead. Tariff and immigration policies proposed by the incoming administration are clouding investor's (and the Fed's) outlook for 2025.
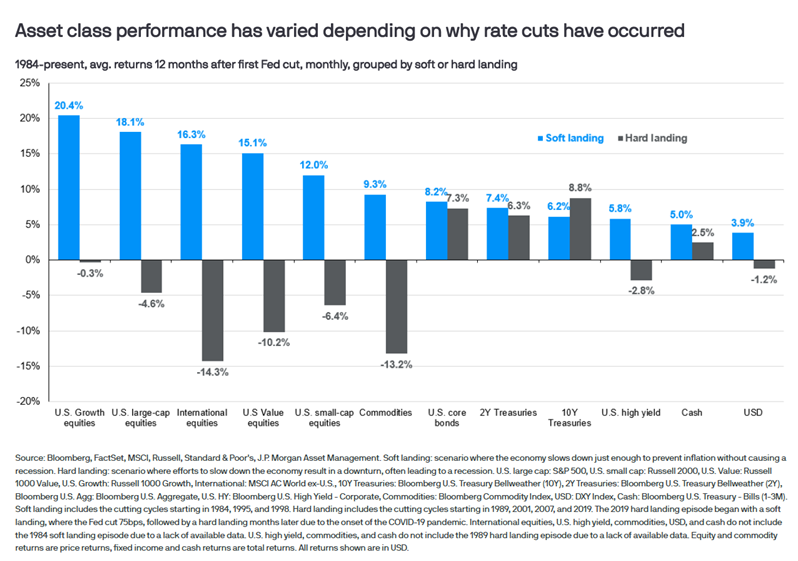
With the Fed still in easing mode, equities should continue to be well supported (remember the old saying, "Don't fight the Fed"). While the Fed's December rate cut was a 'hawkish' cut (a cut with guidance there will be fewer future cuts), we continue to focus not on the number of cuts but more on the overall economic trajectory, which seems to be very resilient right now. With the economy still showing momentum, earnings should maintain their climb in 2025—reinforcing our positive longer-term outlook. However, in the short term, there can always be volatility, and after such a strong year, a little short-term volatility would not be unexpected.
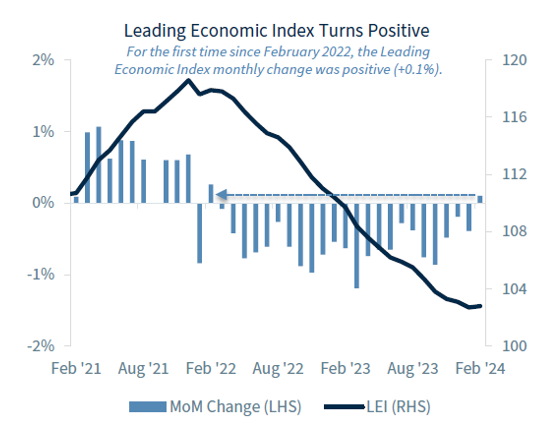
So why doesn't this potential increased volatility scare us very much? A strong consumer! Since the consumer makes up 70% of the U.S. Economy, we are a key ingredient to keep an eye on. The strength of the consumer in 2024 was evident through several key indicators. Consumer spending has shown consistent growth, while consumer confidence remains unshaken, driven by low unemployment rates, steady job growth, and rising wages. There could be some cracks on the horizon for consumer spending. We are starting to see consumers "trade down" a bit in their purchases, meaning they are still happy to spend but on cheaper options for goods and services. There aren't so many cracks to be concerned about yet, but it is certainly an area we watch closely.
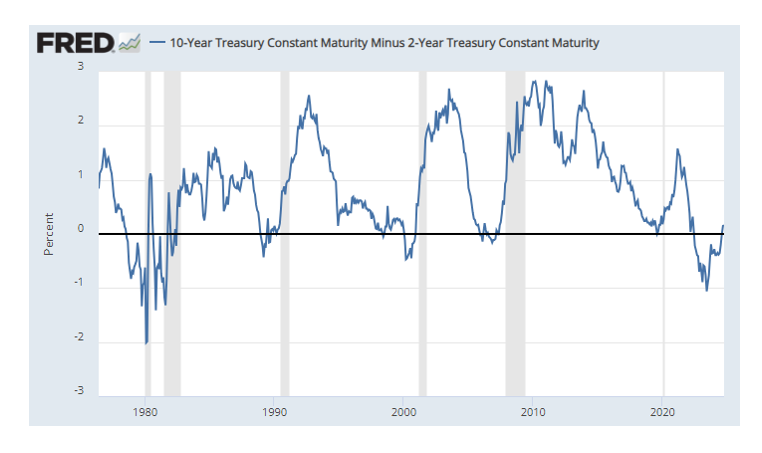
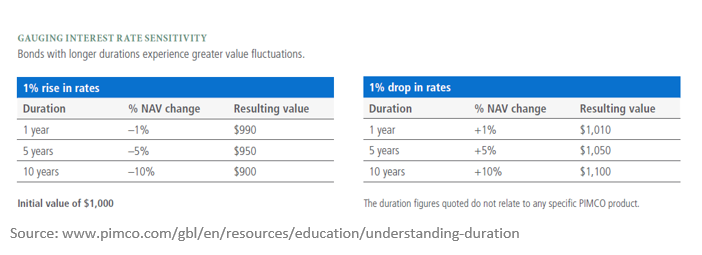
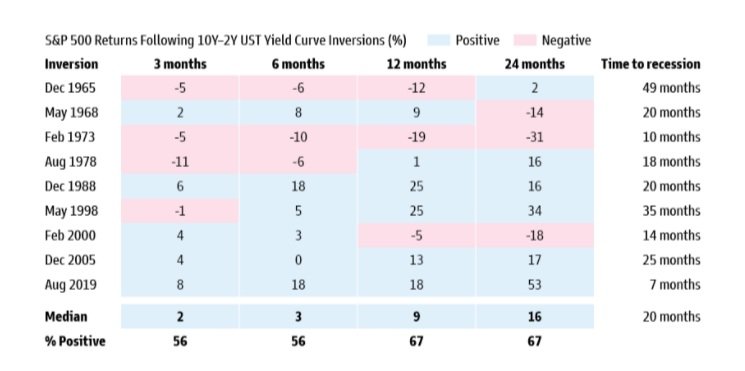
Bonds have had a bizarre year. Coming into 2024, we weren't sure what to expect other than the unexpected. As such, the caution we have exhibited in that portion of our portfolios has helped reduce some volatility in bonds in 2024. Treasury yields have moved contrary to normal historical patterns by rising instead of falling after the Fed started to cut rates in the fall. Better-than-expected economic data and inflation not falling as fast as the market would like to see have challenged investors to reassess the Fed's expected rate path. This means yields are likely to stay a bit more elevated than everyone originally thought. If you look at inflation and employment, the Fed has largely accomplished what it set out to do, even though markets might like to see them do more. The chart below shows where we are versus the Fed's targets.
S&P 500 Price Targets and Return Expectations
Major banks and brokerage firms put out S&P 500 price targets every year, and it may or may not surprise you, but they are rarely accurate. It is impossible to predict something as volatile as the stock market over such a short time. Last year, for example, analysts ranged from bearish to bullish, and the stock market blew straight through every one of their price targets by May.
Stock performance over one year can vary dramatically, but it has been remarkably consistent over the long term.
The other thing on investors' minds right now is…can the performance continue? Of course it can! No one knows for sure if it WILL over the next year (as I said, it is impossible to predict something so volatile as the stock market over such a short time frame), but just because stocks had a tremendous last year does not mean that they must lag the following year. In fact, the statistics show there is essentially no correlation between last year's performance and the next year's performance.
Election Outcome and Markets
As the election dust settles, it is important to remember that the economy is usually the guiding force behind winners and losers in our portfolio. Overall, rising corporate profits, continued economic expansion, and the potential for lower yields later this year provide a potentially positive backdrop for the markets, in our view. Some areas, like international investments, may see additional headwinds from political forces like tariffs or a strong U.S. dollar. At the same time, smaller companies in the U.S. may see some natural tailwinds from continued onshoring and disinflation. While there are many reasons for an optimistic outlook, being prepared for a downturn is evergreen. Our actions in your portfolio will reflect our continued research and developments in these areas as President Trump takes office. There are important things that we need to focus on, as always, such as making sure that you have 6-12 months of expenses set aside in cash so that we can weather any short-term volatility in markets (especially if you are retired), rebalancing to maintain proper diversification and paying close attention to tax loss harvesting and capital gains.
A new administration may provide new risks, but when aren't there risks in investing? With new risks also come new opportunities, and our investment committee meets monthly to ensure portfolios are allocated to take advantage of constantly changing markets. Most importantly, your financial planner here at The Center is here to help you build a financial plan that gives you confidence no matter the market conditions. With that being said, onto 2025!
Angela Palacios, CFP®, AIF®, is a partner and Director of Investments at Center for Financial Planning, Inc.® She chairs The Center Investment Committee and pens a quarterly Investment Commentary.
Nicholas Boguth, CFA®, CFP® is a Senior Portfolio Manager and Associate Financial Planner at Center for Financial Planning, Inc.® He performs investment research and assists with the management of client portfolios.
Any opinions are those of the Angela Palacios, CFP®, AIF® and Nick Boguth, CFA®, CFP® and not necessarily those of Raymond James. The information contained in this report does not purport to be a complete description of the securities, markets, or developments referred to in this material. There is no assurance any of the trends mentioned will continue or forecasts will occur. The information has been obtained from sources considered to be reliable, but Raymond James does not guarantee that the foregoing material is accurate or complete. Any information is not a complete summary or statement of all available data necessary for making an investment decision and does not constitute a recommendation. Investing involves risk and you may incur a profit or loss regardless of strategy selected. The S&P 500 is an unmanaged index of 500 widely held stocks that is generally considered representative of the U.S. stock market. The Russell 2000 Index measures the performance of the 2,000 smallest companies in the Russell 3000 Index, which represent approximately 8% of the total market capitalization of the Russell 3000 Index. The MSCI EAFE (Europe, Australasia, and Far East) is a free float-adjusted market capitalization index that is designed to measure developed market equity performance, excluding the United States & Canada. The EAFE consists of the country indices of 22 developed nations. The Bloomberg Barclays US Aggregate Bond Index is a broad-based flagship benchmark that measures the investment grade, US dollar-denominated, fixed-rate taxable bond market. Keep in mind that individuals cannot invest directly in any index, and index performance does not include transaction costs or other fees, which will affect actual investment performance. Individual investor's results will vary. Investing in oil involves special risks, including the potential adverse effects of state and federal regulation and may not be suitable for all investors. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Diversification and asset allocation do not ensure a profit or protect against a loss. Investing involves risk and you may incur a profit or loss regardless of strategy selected. Past performance is not a guarantee or a predictor of future results. Raymond James and its advisors do not offer tax or legal advice. You should discuss any tax or legal matters with the appropriate professional.